Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, but five-year survival rates are well over 90 percent if it can be caught early enough. Courtesy of Dr. Hao Feng, a Dermatologist at UConn Health, here is a simple ABCDE guide to help you determine if a mole on your skin needs to be checked for cancer.
A stands for asymmetry.
“You do not want something that looks different on one half and different on the other half,” said Dr. Feng.
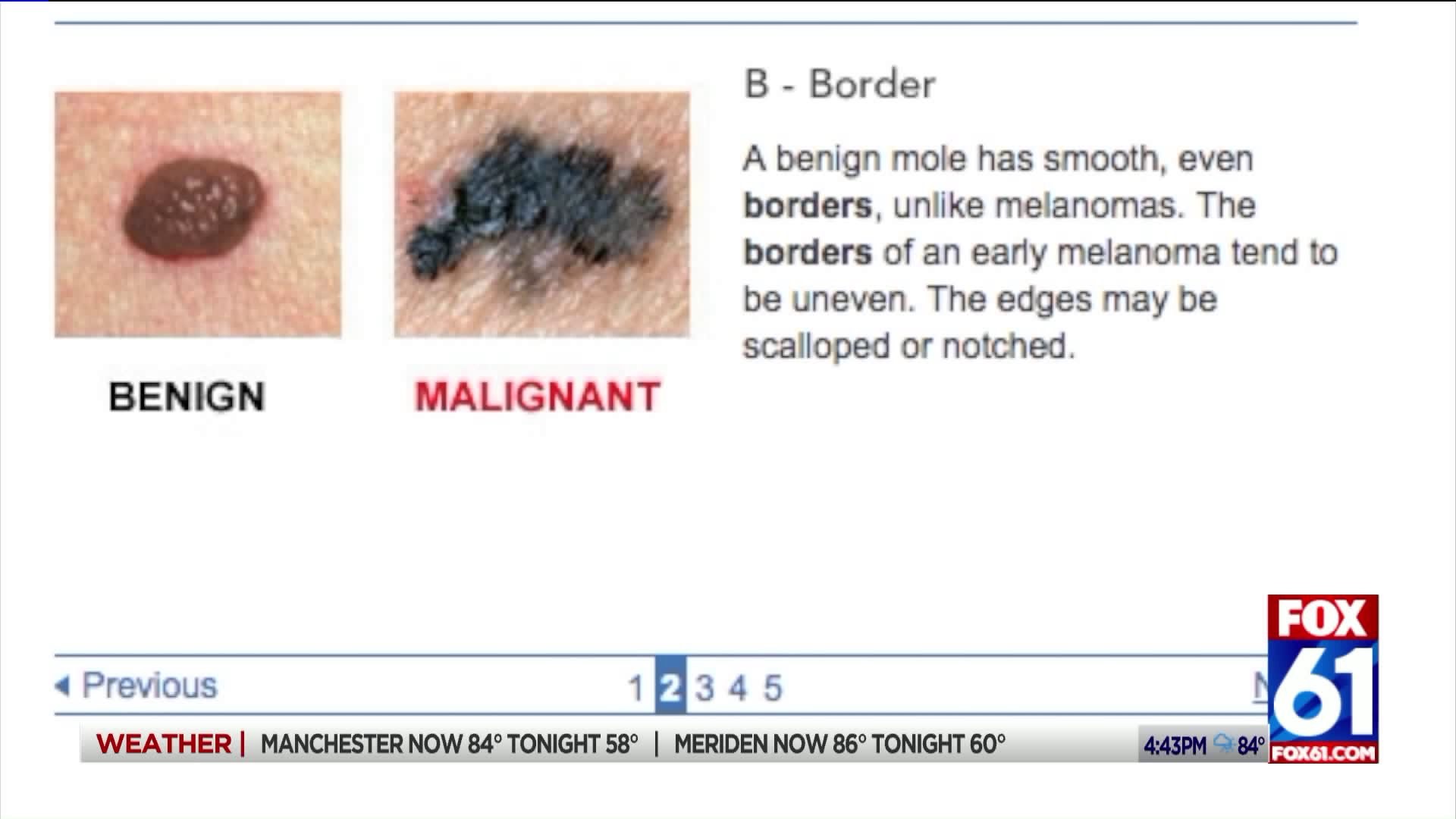
B stands for border.
“You want to have a lesion that has a clearly defined sharp border that’s round,” he said, “you don’t want to see jagged borders that seem undefined … and you don’t want things that look like the coast of Maine.”
C stands for color.
“You want a lesion to have one, or at most, two colors, so maybe a light brown or a dark brown but you don’t want to see a variety of color including red, white or blue,” said Dr. Feng.
D stands for diameter.
“We want lesions to be small, ideally less than the size of a pencil eraser, which is 6 millimeters,” he said.
E stands for evolution.
“So if a spot is changing, bleeding on its own, and just looks different like you have one arm growing out one side, those are all concerning features,” said Dr. Feng.
If a mole has some of these signs, it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s cancerous, but it should be checked out. Normally, that entails having a piece of the mole cut off and biopsied, but UConn Health offers a scalpel-free way of getting your skin checked. It’s called Reflectance Confocal Microscopy.
“Confocal microscopy is a non-invasive imaging technique where we’re able to image the skin on a cellular level, so instead of looking through a microscope you can see it live on a monitor,” said Dr. Feng, “it’s non-invasive, not painful and will save you a biopsy. It works by shining a laser light into the skin and when that light reflects back, we’re able to capture what the cells look like and whether it’s dangerous or not.”